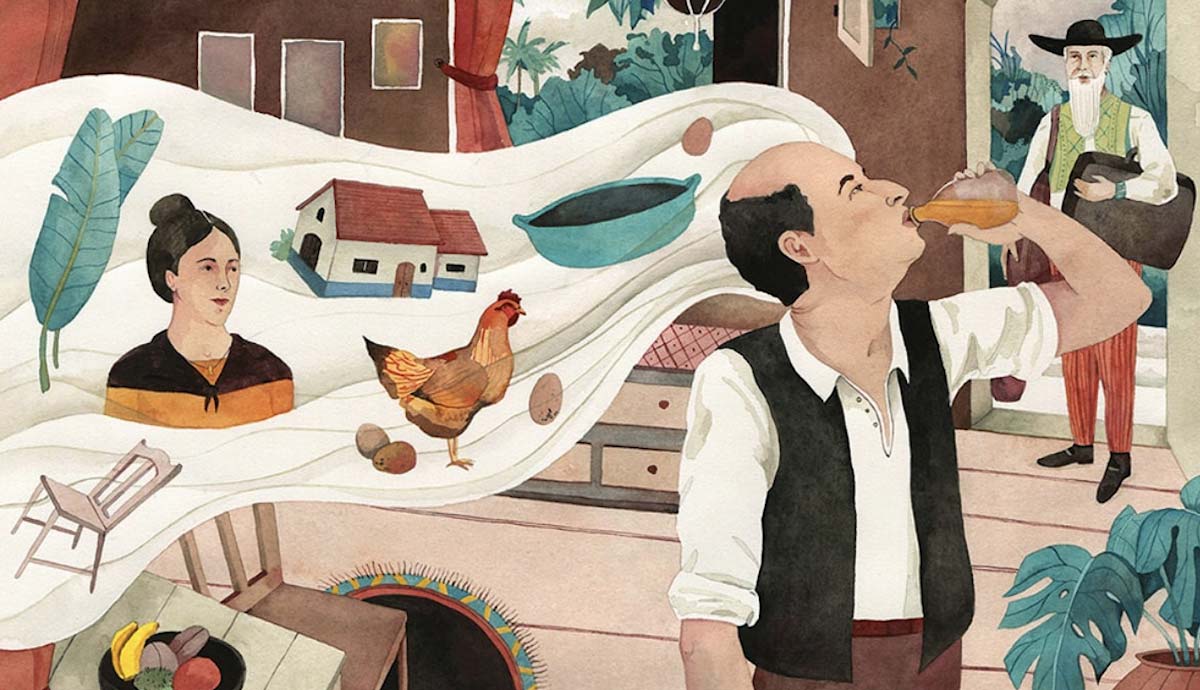
In a particularly striking scene from Gabriel García Márquez’s Nobel prize-winning novel One Hundred Years of Solitude, a trickle of blood takes on a life of its own, flowing from room to room, going around the carpets, crossing terraces, and climbing over curbs as it makes its way across town, unnoticed by all. Notably, this supernatural event is told in a most matter-of-fact language, blurring the line between the real and the magical. This seamless blending of the supernatural into ordinary settings is known as magical realism, and it has been adopted in Latin American literature to defy Eurocentric notions and give marginalized voices a platform. Here are four ways magical realist authors accomplish this.
1. Writing Subalternized Voices Back into History

Magical realism became a potent political instrument for rewriting history from the lens of colonized communities throughout the 1960s and 1970s. Alejo Carpentier, a Cuban writer who introduced the concept of the “marvelous real,” a counterpart to magical realism, famously asked: “After all, what is the entire history of America if not a chronicle of the marvelous real?” For Carpentier and his contemporaries, the intricate realities of Latin America were impossible to depict with conventional forms of literary realism.

Carpentier introduced his theory of the marvelous real as a prologue to his 1949 novel, The Kingdom of This World. Set against the tumultuous backdrop of the Haitian Revolution, the novel offers a subjective perspective on history from a slave’s viewpoint. Carpentier portrays the struggles of enslaved populations of Haiti through the eyes of Ti Noel, the protagonist whose life spans the turbulent events before, during, and after the Haitian Revolution.
Within this narrative, Makandal, an enslaved Black person embodying the Afro-Caribbean hybrid identity, gains recognition for his supernatural powers, becoming a symbol of resistance against colonization. Carpentier’s idea of the “marvelous real” comes to life through this character who has the power to shape-shift into different animals, miraculously evade colonial authorities, and defeat them with potent mountain herbs. By blending historical events with magical occurrences, Carpentier invites the Afro-Caribbean perspective and identity into the retelling of the history of Haiti and its struggle for freedom.
2. Defying Conventional Notions of Time

In his most famous novel, entitled Hopscotch, Argentine author Julio Cortázar allows his readers to hopscotch around the text and read it in multiple chronologies. It is written in the style of stream of consciousness, and the reader has two or three different suggested orders to read the chapters. This provides multiple endings for the book, within a never-ending story of unanswerable questions. For many authors representing Latin America’s literary boom era, such non-linear narratives were a brilliant way to play with Eurocentric and conventional notions of time and history.
With origins in Europe, magical realism gained resonance in Latin America in the 1960s as both an effort to subvert European literary norms and craft narratives that could revise the colonial past. Literary critic Steven Stern notes that the unresolved colonial legacy in Latin America “unsettles unilinear notions of the march of historical time” (1996). The following line from Márquez’s One Hundred Years of Solitude perfectly encapsulates this endeavor: “Melquíades had not put events in the order of man’s conventional time, but had concentrated a century of daily episodes in such a way that they coexisted in one instant.”

Like many other authors from this epoch, Márquez challenges chronology and historical time to suggest that there is no single way of perceiving time. The Colombian author takes the reader from past to present in a non-linear manner over multiple generations of the Buendía family. The novel opens with Colonel Buendía’s execution as he faces the firing squad, as though looking at his past unfold right in front of him while he waits for the reader to catch up to that present moment. It is as if the hundred years in Márquez’s fictional town of Macondo coexisted in that single instant.
This endeavor of unsettling notions of time is far from arbitrary; it grounds itself in the beliefs of many indigenous cultures of Latin America. For the Aymara people of the Andes, for instance, the past lies ahead of us while the future resides behind us. In this stark departure from European frameworks of time, the future remains concealed from view, and one must gesture towards their back to refer to it. The past, however, is visible, lying right before our eyes.
Above all, One Hundred Years of Solitude comments on the cyclical nature of history in the postcolonial experience. The narrative moves back and forth between the past, present, and future. Yet, nothing ever seems to happen in Macondo. There is only solitude.

Marquez’s other famous work of magical realism is Love in the Time of Cholera (1985). The novel tells the story of Florentino Ariza’s spurned love for Fermina Daza, who rejects him to marry Dr. Juvenal Urbino. Stricken with love, Florentino is sent by his mother to the doctor, who diagnoses him with cholera. This is just one instance of the non-realistic depiction of love as a disease colliding with the real world of medicine. Over the span of 51 years, nine months, and four days, Florentino has continued to love none but Fermina when, in a characteristically absurd twist of fate, Dr. Urbino dies while trying to retrieve his pet parrot from a mango tree – and Florentino seizes his chance. While the supernatural themes are not overt, the novel offers a way of seeing the world where the extraordinary is made commonplace.
3. Offering Postcolonial Critique Through Local Cosmogenies

Alongside challenging notions of time, magical realist authors created a space for European and indigenous cosmogenies to intermingle and provide a widened perspective of time, history, and what is considered real. Numerous texts from the Latin American Boom era set out to re-imagine pre-Columbian civilizations and re-articulate postcolonial realities in Latin America. This effort implied weaving pre-Columbian cosmovisions into literary fiction and providing fictional renderings of historical episodes.
In One Hundred Years of Solitude, Márquez provides an account of the tragic event known as the Banana Massacre. The event took place in Ciénaga, Colombia, in 1928, following a labor strike by banana plantation workers, who were demanding improved working conditions. Márquez’s portrayal of the tragic event, in which plantation workers were killed by the Colombian military forces at the behest of the United Fruit Company, challenges the official historical narrative and provides an alternative account. Magical realism, then, as Homi Bhabba puts it, “becomes the literary language of the emergent postcolonial world” (Bhabha, 1990).

The inclusion of pre-Columbian perspectives and cosmogenies further contributed to the creation of this distinctive literary language. This intention is brilliantly exemplified in Julio Cortázar’s The Night Face Up, a short story that blurs the line between dream and reality, past and present. Following a motorcycle accident, the story’s protagonist finds himself drifting between two realms. In one, he is lying on a hospital bed in modern-day Mexico, receiving medical treatment. In the other, he is a captive warrior about to be sacrificed to the gods of a fictional Mesoamerican civilization called Motecas, a witty wordplay between Spanish “motocicleta” (motorcycle) and “Aztecas” (Aztecs).
As the protagonist travels from one world to another, unable to tell which one is real, so does the reader. The ending of the story is nothing short of unexpected. Implicitly, the story seems to suggest that the real world experienced by the protagonist is not the hospital bed in present-day Mexico but rather the ancient world of the Motecas. The protagonist’s accident and his subsequent treatment in the hospital is, in fact, the hallucination or the dream. With this reversion of historical time, Cortazar poignantly re-inserts a pre-Colombian perspective back into history to disturb Eurocentric perceptions of time. This comes as a subtle wink to the implied reader, playfully teasing their expectations.
4. Reclaiming Female Stories Through Magical Realism

While male voices dominated magical realism in Latin America throughout the 1960s and 1970s, a feminist approach did not take too long to emerge, the most vivid example being Isabel Allende’s bestselling 1982 novel The House of the Spirits. Released 15 years after the original publication of One Hundred Years of Solitude, the novel has often been interpreted as the feminist counterpart to the quintessential Latin American magical realist novel.
Originally written as a letter to her dying grandfather during her time in exile in Venezuela, Allende’s novel interlaces magic and the female experience to address the country’s complex socio-political realities. In an interview, Allende mentions that she wanted to write a letter to her grandfather so she would not forget her family’s history. As the niece of the former Chilean President Salvador Allende, who tragically ended his life during the coup orchestrated by General Augusto Pinochet, the writer experienced firsthand the effects of the subsequent military dictatorship and exile.

As a magical realist text that weaves a multi-generational story, comparisons were inevitably drawn between The House of Spirits and One Hundred Years of Solitude. Markedly centered around women, however, Allende’s text goes beyond mere imitation. The Chilean writer creates a stellar parody of Márquez’s text while putting female characters and their magical abilities at the core of her narrative. The unmistakable magical realist cues interwoven in the novel serve as a witty nod to the Márquezian world but masterfully transcend it by drawing upon a distinctively female perspective.
The House of Spirits, which propelled Allende to international bestseller status, remains one of the most prominent magical realist novels that intends to write female voices back into history and the genre. Amid the backdrop of political events and social injustices, Allende weaves in magical occurrences, clairvoyance, and spirituality, masterfully writing women as a “site of history” (Foreman, 1992).

Another notable work that took the magical realist route to delve into feminist perspectives is Like Water for Chocolate (1992) by Mexican Laura Esquivel. Set in Mexico, it follows Tita de la Garza and her passionate relationship with Pedro Muzquiz. The two are prevented from marrying due to a Mexican tradition that the youngest daughter must remain unmarried and look after her mother until her death. Pedro, therefore, marries Tia’s eldest sister, Rosaura, to remain close to Tita. Meanwhile, Tita, who was mostly raised by the family cook Nacha, expresses her pent-up emotions through food, and each of the 12 chapters of the novel includes a Mexican recipe that is related to Tita’s life. In the second chapter, she makes a wedding cake for Rosaura and Pedro’s wedding, crying into the batter. This causes everyone, except for Tita, to become violently ill. The lovers are kept separate for over two decades, but when they are finally united, their love story has a magical end.
While pioneered by Latin American writers, magical realism has expanded beyond its origins to become a mainstay in world literature. This expansion coincided with growing interest in multiculturalism and postcolonial studies as writers recognized the genre’s ability to explore complex identities, histories, and realities. Works like Salman Rushdie’s Midnight’s Children and Toni Morrison’s Beloved demonstrate how magical realism can address the universal themes of identity, memory, and trauma.
References:
- Bhabha, K. H. (1990). Nation and narration. Routledge.
- Foreman, G. (1992). Past-on stories: History and the magically real, Morrison and Allende on call. Feminist Studies 18(2), 369–88.
- Stern, J. S. (1996). The tricks of time: Colonial legacies and historical sensibilities in Latin America. The Princeton University Library Chronicle, 57(3), 371–92.